Codewars 문제풀기 (05/05)
Bouncing Balls
-
높이 h에서 공을 떨어뜨린다. 공은 바닥에 닿고 튀어 오르는데 h의 2/3만큼 다시 튀어오른다(bounce = 0.66), window높이에 있는 사람은 공을 몇번 볼 수 있는지 리턴해라
-
h는 0보다 커야하고, bounce는 0~1, window는 h보다 작아야한다. 어느 조건도 만족하지 못한다면 -1을 리턴한다.
h = 3, bounce = 0.66, window = 1.5 👉 bouncingBall(3.0, 0.66, 1.5) 👉 3 h = 30, bounce = 0.66, window = 1.5 👉 bouncingBall(3.0, 0.66, 1.5) 👉 15 h = 3, bounce = 1, window = 1.5 👉 bouncingBall(3.0, 0.66, 1.5) 👉 -1
1. Test와 리팩토링
-
테스트 1 - 입력 조건을 만족하지 못하면 -1을 리턴한다.
-
테스트 코드
@Test public void testShouldReturnNegative1WhenConditionNotMet() { // Given: Set condition not fulfilled double h = 0; double bounce = 2; double window = 5; // When: Call bouncingBall method int actual = BouncingBall.bouncingBall(h, bounce, window); // Then: Should return -1 assertEquals(-1, actual); } -
실제 코드
public class BouncingBall { public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) { if (h <= 0 || bounce <= 0 || bounce >= 1 || window >= h;) { return -1; } return 0; } } -
리팩토링 - if문 check부분을 메서드로 추출
package bouncingBalls_20200505; public class BouncingBall { public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) { if (isFulfilledCondition(h, bounce, window)) { return -1; } return 0; } private static boolean isFulfilledCondition(double h, double bounce, double window) { return h <= 0 || bounce <= 0 || bounce >= 1 || window >= h; } }
-
-
테스트 2 - h=3.0, bounce=0.66, window=1.5 이면 3을 리턴한다.
-
테스트 코드
@Test @DisplayName("test should return 3 when h=3.0, bounce=0.66, window=1.5") public void test1() { // Given: Set condition double h = 3.0; double bounce = 0.66; double window = 1.5; // When: Call bouncingBall method int actual = BouncingBall.bouncingBall(h, bounce, window); // Then: Should return 3 assertEquals(3, actual); } -
실제 코드
public class BouncingBall { public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) { if (isFulfilledCondition(h, bounce, window)) { return -1; } int count = 0; while (Math.pow(bounce, count) > window / h) { count++; } return count * 2 - 1; } private static boolean isFulfilledCondition(double h, double bounce, double window) { return h <= 0 || bounce <= 0 || bounce >= 1 || window >= h; } }- 식을 계산해보면 처음에 h높이에서 떨어지면 h * 0.66 만큼 튀어오르고, 다시 떨어지면 h * 0.66² 만큼 튀어오른다. 그래서 h * 0.66^n 이 window높이보다 작아지면 window에서 공을 더이상 볼 수 없다. 공은 튀어오를때 한번, 최고점에 오른 후 다시 떨어질 때 한번, 한번 튀어오를때 두번 볼 수 있고, 처음 떨어질 때 1번 볼 수 있으니 count * 2 -1로 계산했다.
-
리팩토링 - 반복문을 수학식으로 표현
package bouncingBalls_20200505; public class BouncingBall { public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) { if (isFulfilledCondition(h, bounce, window)) { return -1; } int bounceCount = (int) (Math.log10(window / h) / Math.log10(bounce)); return bounceCount * 2 + 1; } private static boolean isFulfilledCondition(double h, double bounce, double window) { return h <= 0 || bounce <= 0 || bounce >= 1 || window >= h; } }-
수식으로 나타내면
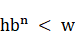
이 식을 만족하는 n * 2 +1을 하면 된다. (b는 bounce, w는 window)
n으로 나타내면 결국
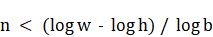
이다.
-
-
2. 답 비교, 느낀점
Best Practice 가장 많이 받은 코드
public class BouncingBall {
public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) {
if ((h <= 0) || (window >= h) || (bounce <= 0) || (bounce >= 1))
return -1;
int seen = -1;
while (h > window) {
seen += 2;
h = h * bounce;
}
return seen;
}
}
- while문을 이용해서 계산했다.
- 본 횟수를 -1로 초기화 해서 계산했다.
그 외 신박하다고 생각한 코드
public class BouncingBall {
public static int bouncingBall(double h, double bounce, double window) {
if (h <= 0 || bounce <= 0 || bounce >= 1 || window >= h) {
return -1;
}
return 2 + bouncingBall(h * bounce, bounce, window);
}
}
- 재귀 함수로 해결했다. 조건에 만족하지 않으면 -1 하기 때문에 결국 최종 계산에서 -1을 해서 답이 나온다.

댓글남기기